4 common 3D printing mistakes
While 3D printing can be a fascinating endeavor, it can also be quite frustrating. According to the educational platform Makers Empire, its students often feel disheartened because printing even a small object can take up to 30 minutes, and the final 3D model may not turn out as envisioned.
To avoid a negative experience, you must be aware of 3D printing principles, material intricacies, and modeling techniques. Below are the most frequent mistakes that newcomers can make.
FAQ: What precautions should you take when 3D printing?
When engaging in 3D printing, it’s crucial to prioritize safety. Ensure your workspace is well-ventilated, particularly when using materials that may emit fumes. Fire safety is also necessary, so have a fire extinguisher and never leave your printer unattended during operation. Properly position your 3D printer on a stable, non-flammable surface, and handle hot components with care, using safety gear when necessary.
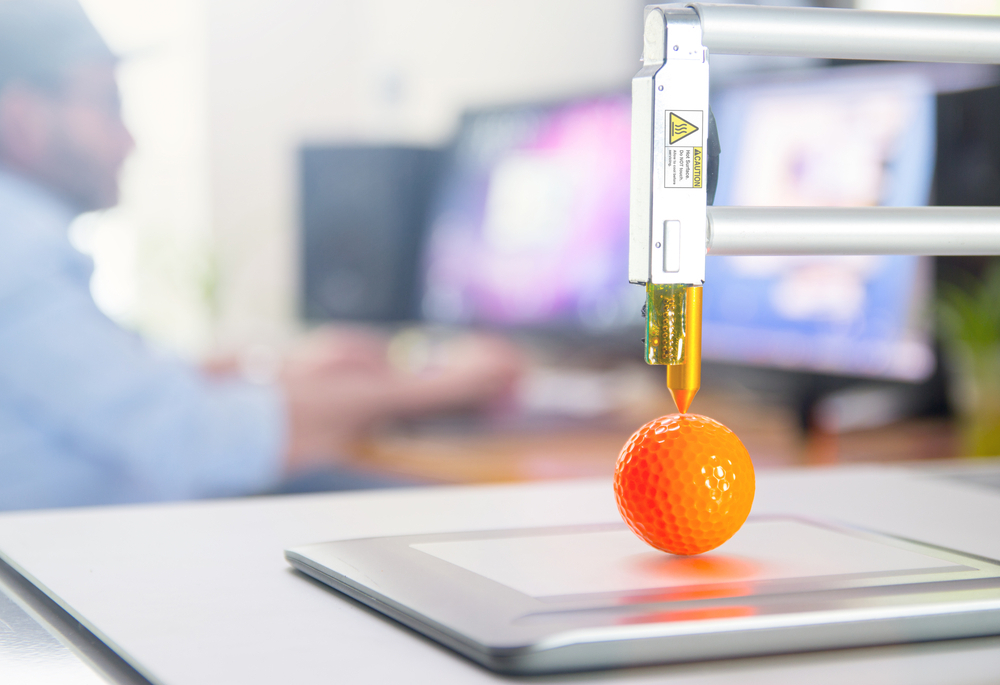
Mistake #1: Not taking the properties of materials into account
There are 10+ different materials available for 3D printing. These can be plastics, metals, ceramics, resins, and others. Each material comes with its unique set of properties. For example, working with plastics is relatively easy, and the resulting models tend to be durable. On the other hand, metal 3D printing is frequently used in industrial production and can be quite challenging for beginners to handle.
Below are useful tips on working with printing materials properly:
- Learn material specifications. Even if you work with one specific substance, its properties may vary depending on the manufacturer. Thus, it’s recommended to explore the provided specifications in advance. You can find material information on the producer’s website, thematic forums, and official databases. Also, search for features of each specific material like plastic or ceramic with the filament properties table.
- Ensure optimal printing temperature for each material. First, refer to the manufacturer’s specifications, and then start testing. Baseline numbers may differ based on the material’s properties. For example, polylactic acid (PLA) can be printed at around 190–220°C, while ceramic measures vary from 1,000 to 1,600°C.
- Check for moisture. If filaments absorb too much moisture, this can cause poor quality due to extrusion problems, weaknesses, and delamination. Moreover, this can decrease the lifespan of ready-made models.
- Experiment with print speed. Since 3D printing materials are different, it influences the working process. For example, polylactic acid typically performs well at moderate speeds, while acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) requires slower speeds due to its higher melting points and tendency to warp.
If you need help deciding which material to begin practicing with, consider working with 3D-printed nylons. Such models are stronger and more durable than those made from PLA or ABS.

Recent Comments